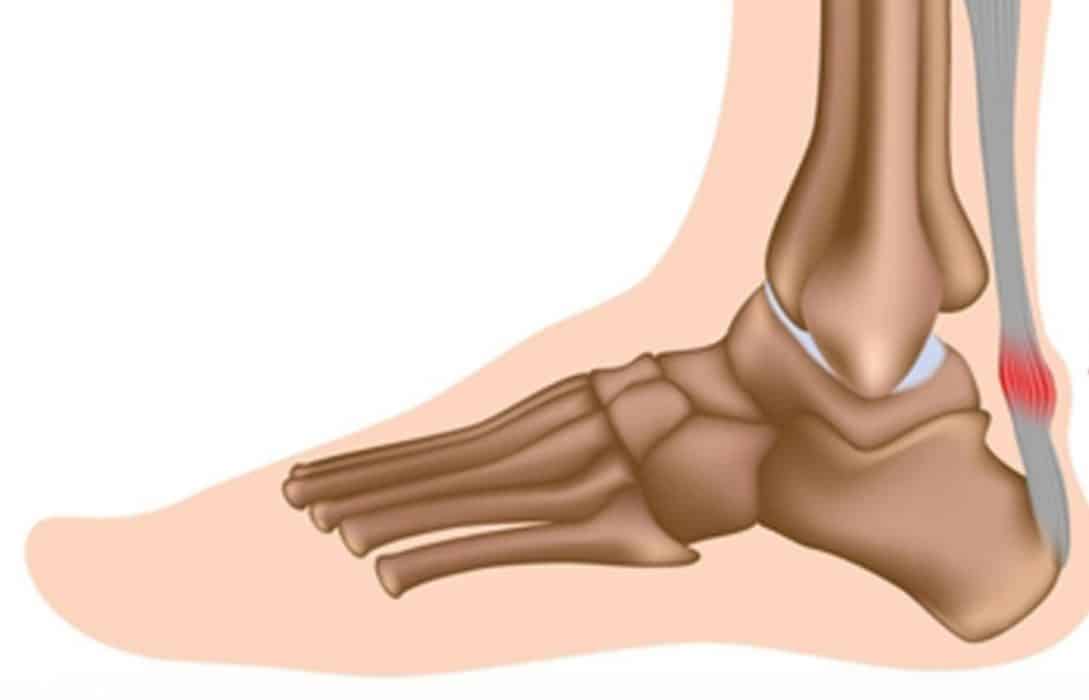
If you have ever been told you have a tendinopathy or heard the term, you may be asking yourself: What is it exactly and how did I get it? In this article, Physiotherapist Tim from our Morphett Vale practice aims to provide you with a clear understanding of how tendinopathies are caused, signs and symptoms of them, as well as how a physiotherapist can help with rehabilitation.
Anatomy and Physiology
Tendons are structures in your body which connect muscle to bone. These are often confused with ligaments which connect bone to bone. Tendons are made up of several components including tenocytes (tendon cells), collagen and proteoglycans (proteins). There are also nerves and blood vessels dispersed throughout it which provide nutrients and innervation/sensation (Millar et al. 2021). Tendons are responsible for transmitting movement to your bones and act to store and deliver forces (Roberts, 2002) such as those absorbed by your Achilles tendon (back of the ankle) when you’re walking. The absorption of forces when you plant your foot when walking is stored in the tendon and are released when you push off to take your next step.
What Causes a Tendinopathy?
A tendinopathy (sometimes called tendinosis or tendinitis) can be caused by several factors, however, in most cases they are caused by overuse. Essentially, you have performed too much too soon. For example, in the clinic, we see many people develop a tendinopathy after restarting running or the gym after a very long period of sedentary behaviour. The tendon simply doesn’t have the capacity for what you are asking it to do. Therefore, we will always start exercise gradually when beginning a new or more intense program which allows the tendon to adapt correctly. Other factors such as some medications (steroids and statins), smoking status, age, obesity and diabetes can increase the risk of developing a tendinopathy (Millar et al. 2021).
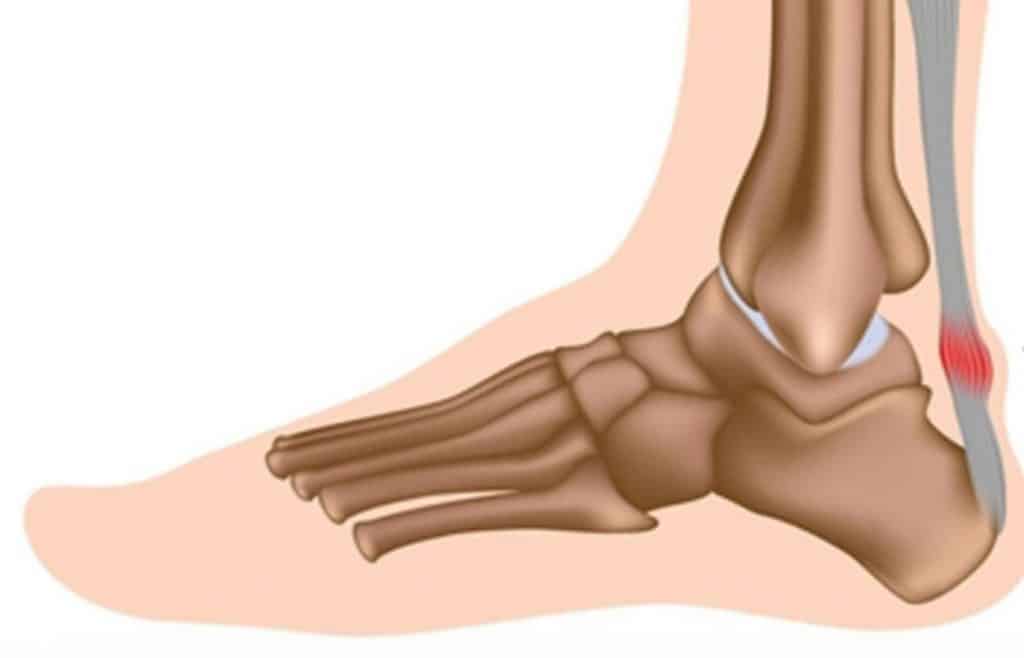
Signs and Symptoms of Tendinopathies
The most common areas to develop a tendinopathy include the shoulder (5.5% of general population) and the hip (4.2% of the population), however, they also appear commonly in the ankle/foot, elbow and knee (Millar et al. 2021). Common colloquial tendinopathies you may have heard of include tennis and golfer’s elbow, runner’s and jumper’s knee and rotator cuff pain.
How will you know if you have developed a tendinopathy? Commonly people report pain after exercise, improving pain during exercise, tenderness over the tendon when touching it (often a very specific location) and sometimes swelling and crepitus (audible noise) (Brukner et al. 2012).
How Do I Rehabilitate A Tendinopathy?
One of the most effective and commonly used rehabilitative tools for a tendinopathy is a specific loading program (progressive strengthening) for the injury site with appropriate management advice (Mellor et al. 2018; Breda et al. 2021; Wilson et al. 2018). This often consists of exercises performed in a specific way aimed precisely to the injured tendon with education on how to avoid reinjury. Studies suggest that exercise may promote the production of collagen fibres within the tendon which gradually repairs the sustained damage over time among many other processes. Often exercise also provides a substantial amount of pain relief which can be very beneficial especially if your injury has become chronic. Your physiotherapist is trained to help you with these exercises that can be performed at home or in the gym.
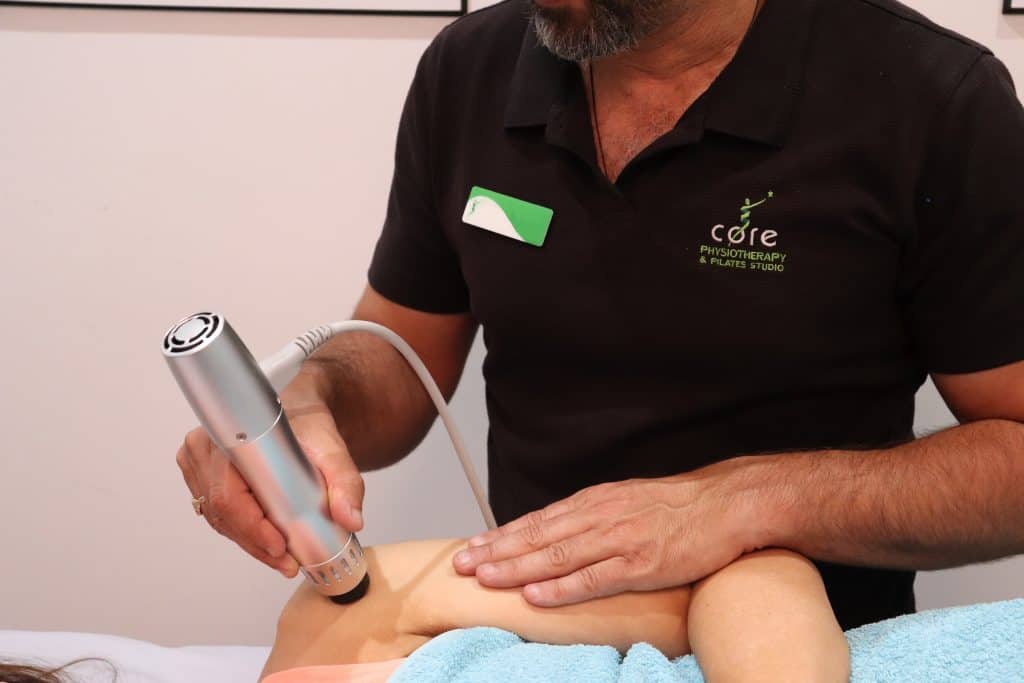
Other treatment modalities include shockwave therapy (van Leeuwen et al. 2009; Korakakis et al. 2018), dry needling (Stoychev et al. 2020) and manual therapy such as massage. In most cases tendinopathies are rehabilitated well in the clinic with the help of your physiotherapist, however, occasionally more intensive approaches are required if this conservative management fails. Your physiotherapist will discuss with you on alternative treatment options if needed. These may require a referral to another healthcare professional.
In summary, a tendinopathy is an injury to a tendon which is often caused by doing too much too soon. Symptoms often present with localised pain over the tendon and improved pain with exercise. These can occur in many areas of the body and can be managed with an appropriate exercise program and education. Other treatment options exist and can be used in conjunction with an exercise program with help from your physiotherapist.
This blog was written by Tim Jennings (Physiotherapist), from our Morphett Vale practice.
References
Breda, SJ, Oei, EHG, Zwerver, J, Visser, E, Waarsing, E, Krestin GP, et al. 2021, ‘Effectiveness of progressive tendon-loading exercise therapy in patients with patellar tendinopathy: a randomised clinical trial’, British Journal of Sports Medicine, vol. 55
Korakakis, V, Whiteley, R, Tzavara, A, Malliaropoulos, N 2018, ‘The effectiveness of extracorporeal shockwave therapy in common lower limb conditions: a systematic review including quantification of patient-rated pain reduction’, British Journal of Sports Medicine, vol. 52
Mellor, R, Bennell, K, Grimaldi, A, Nicolson, P, Kasza, J, Hodges, P, et al. 2018, ‘Education plus exercise versus corticosteroid injection use versus a wait and see approach on global outcome and pain from gluteal tendinopathy: prospective, single blinded, randomised clinical trial’, British Medical Journal, vol. 361
Millar, NL, Silbernagel, KG, Thorborg, K, Kirwan, PD, Galatz, LM, Abrams, GD, et al. 2021, ‘Tendinopathy’, Nature Reviews, vol. 7, no. 1
Roberts, TJ 2002, ‘The integrated function of muscles and tendons during locomotion’, Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular and Integrative Physiology, vol. 133, no. 4
Stoychev, V, Finestone, AS, Kalichman, L 2020, ‘Dry needling as a treatment modality for tendinopathy: a narrative review’, Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine, vol. 13, no. 1
Van Leeuwen, MT, Zwerver, J, van den Akker-Scheek, I 2009, ‘Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for patellar tendinopathy: a review of the literature’, British Journal of Sports Medicine, vol. 43, no. 3
Wilson, F, Walshe, M, O’Dwyer, T, Bennett, K, Mockler, D, Bleakley, C 2018, ‘ Exercise, orthoses and splinting for treating Achilles tendinopathy: a systematic review with meta-analysis’, British Journal of Sports Medicine, vol. 52